As of December 8th, web tracking settings are introduced to Messenger as part of digital user tracking configuration (formerly known as journey tracking). Administrators can enable, configure customized tracking per website or business context, and deploy web tracking directly within Messenger.
This enhancement brings granular control and helps organizations align tracking behavior with varied compliance, operational, or experimentation needs.
A Flexible and Customizable Configuration Experience
Previously, web tracking settings were only available under Predictive Engagement, where a single configuration applied globally across all deployments. Organizations could not tailor tracking rules for individual sites, business units, or test environments.
With the new Messenger-based configuration model, administrators can now create and assign unique tracking settings for each Messenger Configuration, enabling:
- Support for multiple websites with distinct tracking requirements:
A microsite may collect attribution data, while an authenticated portal may require strict privacy filters.
Refined tracking behaviors for more accurate representation of user journeys
By default, digital user tracking captures all visitor navigation, which is sufficient for many scenarios. However, when finer filters or privacy considerations are required, Messenger's web tracking settings offer targeted control.
1. Exclude IP Addresses: Filter Out Unwanted Traffic
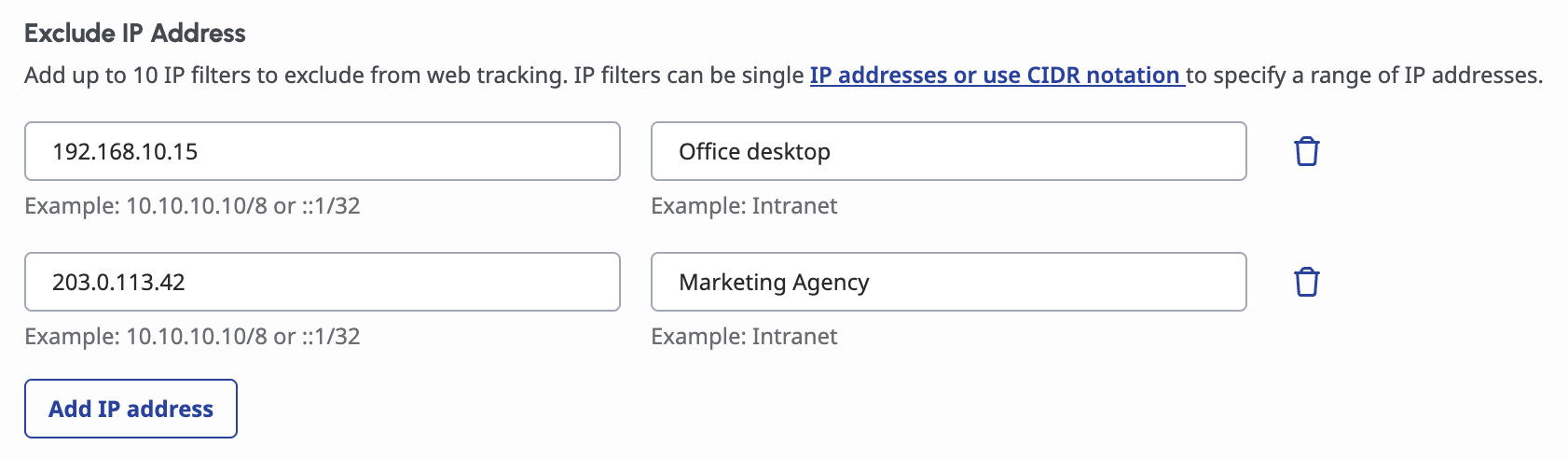
Administrators can exclude individual IP addresses or IP groups to prevent the collection of internal or non-customer data. Their data will no longer be collected to prevent tracking unwanted employee navigation and mixing internal traffic with actual customer traffic.
Common applications include:
2. Exclude URL Query Parameters: Omit Non-Essential or Sensitive Data

URL Query Parameters appear in a website's URL. They usually store values. Since digital user tracking treats every URL change as a page view, excluding irrelevant or sensitive parameters helps maintain cleaner, more meaningful journey data.
Common applications include:
-
Marketing attribution parameters (e.g., utm_campaign, ad_id):
Prevent a single page from appearing as multiple distinct visits when a visitor accesses it from different sources such as a newsletter, an online ad etc.
3. Track URL Fragments: Capture Fragment-Based Navigation
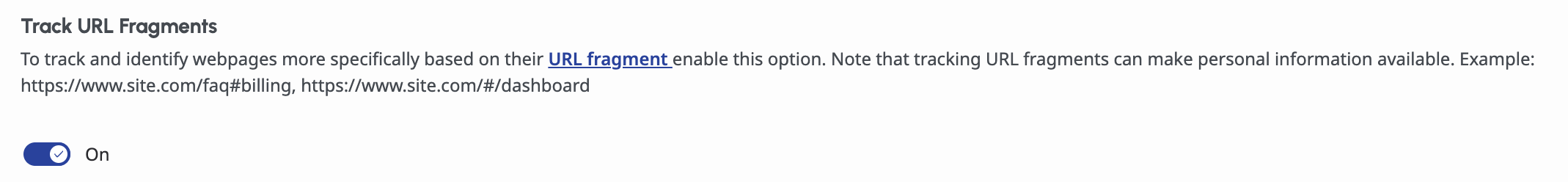
URL fragments (the part of a URL after #) can represent anything from page sections to application state:
4. Track Site Searches: Record terms searched by visitors
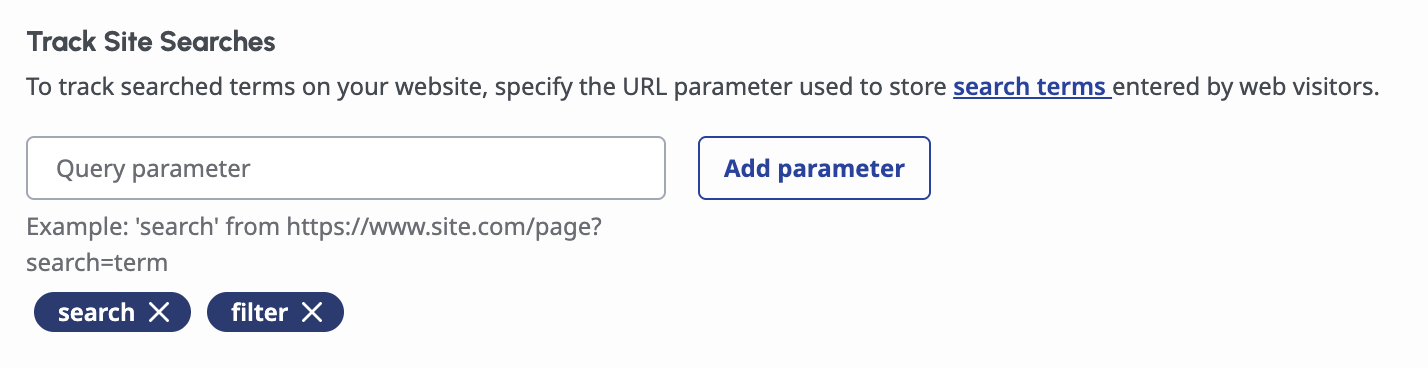
Some websites store user search terms in query parameters (e.g., ?q=pricing). By registering these parameters in Messenger, search activity is properly recorded as a Search event rather than a navigation entry.
There are multiple types of searches that can be tracked with this setting:
-
Advanced Search:
Retailers and marketplaces often support multi-attribute searches (category, color, size, availability). Those user preferences are often stored in multiple query parameters and reflect customer needs or constraints.
Useful Links
Please check out the resources below to learn more and get started:
------------------------------
Mai-Christine Hoang
Product Manager
------------------------------